Data Analysis has become an integral part of running a smooth and successful business. This is because when the analysis of data is done effectively, it not only gives you a better understanding of your business’s previous performance but, you can make better future decisions too.
There are many different data analysis tools available to help you make sense of your data. Some of these tools are designed for specific types of data, while others are more general purpose. Choosing the right tool for your needs will depend on the type and amount of data you have, as well as your goals for analyzing it.
There are basically four types of data analysis and you can utilize them at all levels of your company’s operations.
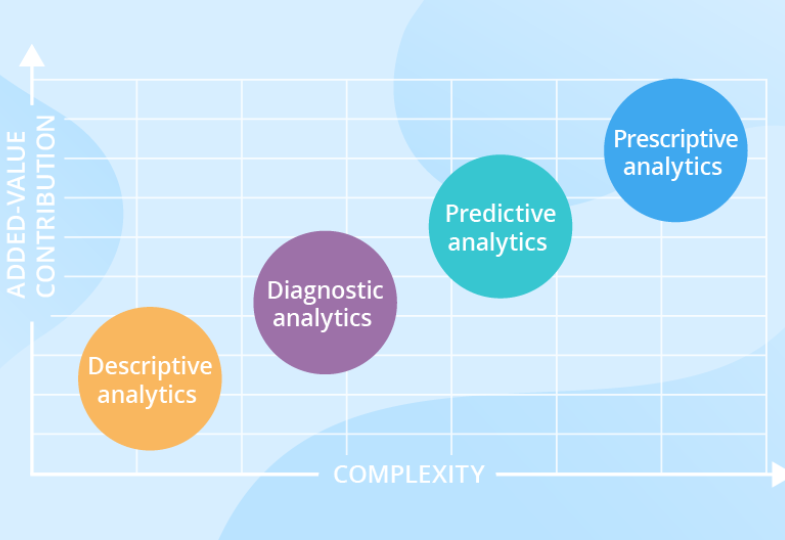
The four types of data analysis are:
While we are separating these into categories, all of these are related and build-up on one another. Likewise, as we move from the simplest type to comparatively complex one, you will face an increase in the degree of difficulty and resource required.
Fortunately, the level of added insight and value also increases.
It is the most common and simplest use of data in the industry. In simple terms Descriptive Data Analysis answers “what happened” by summing up past data.
It simply describes what has happened and doesn’t try to explain why it might have happened. Furthermore, it does not try to establish cause-and-effect relationships and aims to provide just an easily digestible snapshot.
Some good examples of descriptive data analysis in action can be Google Analytics or any other social media analytics.
There are mainly two techniques used in descriptive data analysis:
Simply gathering data and presenting it in a summarized format is data aggregation.
To give you a clear example, an e-commerce has a hold of all kinds of data relating to their website or page visitors and customers. The summarized data, or aggregate data can provide an overview of the wider data set. For instance, the average number of purchases or the gender of the customer.
This is the analysis part. Data Mining is when the analyst explores the data and tries to uncover any trends or patterns.
The outcome of Decriptive Data Analysis is a visual representation of data as a pie chart or a bar graph.
After “what happened” is answered, the succeeding step is delving deeper and as “why it happened?”
Diagnostic Data Analysis takes the insights from descriptive data analysis and dives down to find the causes for those outcomes. This type of data analysis is mostly used to create more connections between data as well as identify behavior patterns.
To give you a clear indication of how diagnostic analysis is performed, here is an example:
Your website or page may have a healthy volume of website visitors and many visitors may have used the add to cart action. However, there might be a drop in sales occurred because very few visitors actually proceeded to make a purchase.
In order to get to the root cause of this, the analyst has to drill down further on this information. Upon further inspection, it surfaces that most of the visitors abandoned ship when it came to filling their phone numbers.
Now, the analyst may find that there were some problems in the contact information form.
See, how with a little bit of digging, the analyst went closer to finding an explanation for the data anomaly.
However, diagnostic data analysis is not only about finding or fixing problems, you can also use it to see the cause of positive results. You may find that your visitor number significantly increased on any month and you can delve to find about the campaigns that you might have run during that month that caused it.
This will help you to determine what type of campaign will be suitable for you to achieve your goals.
Predictive Data Analysis aims to answer the question “what is likely to happen”. It tries to do so by using previous data to make predictions about the future outcomes.
It is a step up in terms of data analysis to the previously discussed types of data analysis as it uses the insights from descriptive and diagnostic data analysis to make a logical prediction of the future outcome of events.
It uses the relationship between a set of variables to make the predictions. For instance, if you own a restaurant, you might decide to get an extra delivery driver on weekends, as your predictive model tells you that your takeaway orders are likely to rise on a typical Saturday night.
The predictive model does so by looking at the average number of takeaway orders during Saturdays as compared to other days.
Also, you can use predictive data analysis for classification. You can predict whether the customer can pay back the credit, if you are working in a credit-card company, by looking back at his/her track record.
And, now you can classify whether or not a client is eligible for a credit card.
Furthermore, Machine learning is also a branch of predictive data analysis. Machine learning models are designed to identify patterns in the data and evolve automatically to make more accurate predictions.
This is similar to how we humans use predictive models to forecast possible future outcomes.
Although the predictive data analysis model is not hundred percent accurate, it eliminates most of the guess work. This is crucial while determining the best course of action and making business decisions.
Some of the business applications of predictive data analysis are:
This is the most sought after type of data analysis, however, very few organizations are equipped to perform it. Prescriptive Data Analysis is the frontier of data analysis as it determines the course of action that takes in the current decision or problem, by combining the insight from all previous analyses.
It is a huge organizational commitment to utilize Prescriptive Data Analysis as it requires state of art data practices and technology. Your company must be sure that they are ready and willing to put forth the resources and effort.
It is, without doubt, the most complex type of analysis. It shows you how you can take the best advantage of the predicted future outcomes.
Likewise, questions like ‘what steps can be taken to avoid future problems?’, and ‘how can you capitalize on emerging trends?’, are also answered using prescriptive analytics.
The prescriptive data analysis involves algorithms, machine learning, computational modeling procedures and statistical methods.
Basically, a prescriptive analytics model considers all future decision pathways or patterns that your company might take and their possible outcomes. This is beneficial for you as you can see how each combination of decision your company makes might affect the future.
Moreover, based on all possible outcomes, the company can decide what is the best possible route to take.
Sign up to stay updated with the latest insights, news, and more.